Eight years and $2 billion [1] – this is the least that an average drug company spends to develop a drug. Even after this, the chances of failure are quite high as only 1 out of 10 gets regulatory approval. AI can boil down the time spent and reduce the cost. It can help to create safer and efficacious drugs and it has proved its mettle when immunologists created vaccines for Covid-19 with its inputs. But this is just one of the benefits of AI in healthcare.
AI’s value in healthcare could become $188bn [2] by 2030. In 2021, it was just around $11bn. This growth is an indicator of how AI has started impacting the healthcare industry across strata. From drug discovery to smart gadgets to diagnose patients, robotic surgeries, patient data management, and others, businesses have started to realize how good AI is and are leveraging it.
Let’s take a deep dive to know what is happening.
How AI benefits healthcare operations?
AI has the potential to revolutionize how healthcare is delivered and managed by harnessing the power of advanced algorithms and machine learning. From efficient data management and diagnostic assistance to personalized treatment and predictive analytics, AI solutions can enable healthcare providers to make better-informed decisions, improve patient outcomes, and enhance operational efficiency.
AI can also help by automating administrative tasks, introducing virtual healthcare assistants, and even contributing to drug discovery and development. The pros of AI in healthcare are so pervasive that it can quickly reshape the landscape of healthcare operations and open new frontiers of possibilities for the future.
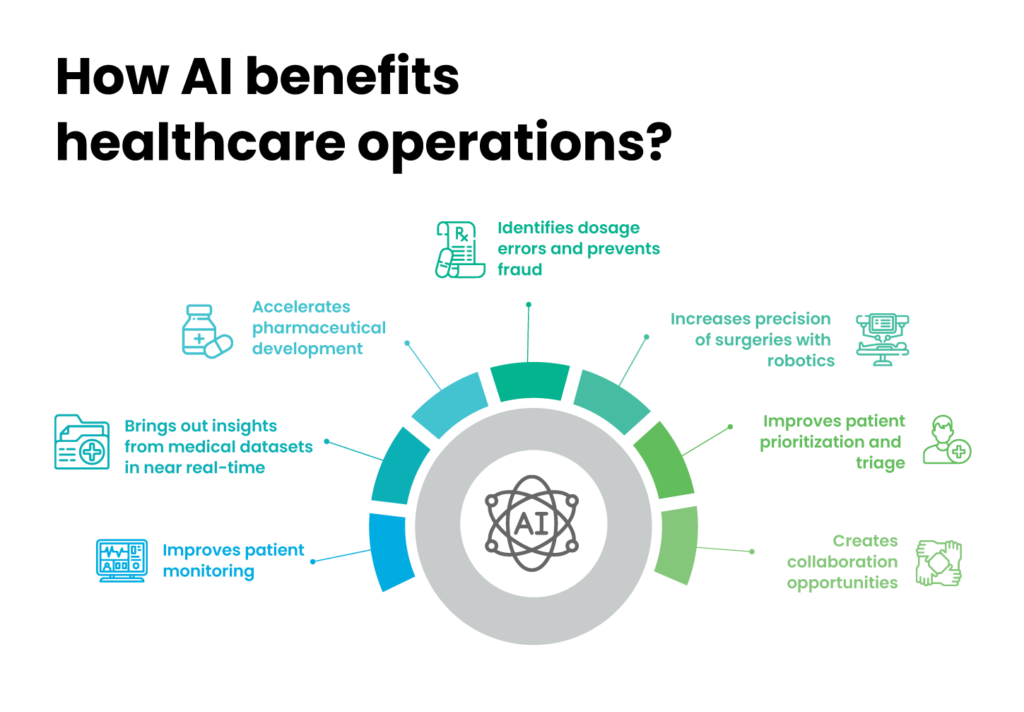
1. Improves patient monitoring
AI has transformed the patient monitoring system for better. With smart wearables, it has made early symptom detection, dosage monitoring, analysis of data for anomalies, special care for geriatric populations, and other things possible.
Smart wearables have helped departments like emergency to work more efficiently. These have made the round-the-clock monitoring of critical patients easier. The sector is also benefitting from the reducing chances of manual error and loads of care providers.
In the last couple of years, there were a few instances where smart wearables raised timely alerts regarding cardiac arrhythmia and gave doctors more time to save patients. Apps to measure glucose level and calories are also becoming popular among athletes, senior citizens, health enthusiasts, and patients with critical illness.
In low-resource locations, delivering proper care is nearly impossible due to the lack of medical assistants and infrastructure. There, telemedicine solutions can transform how healthcare operates.
Telemedicine have proved its efficacy during the pandemic when there was constraints in visiting hospitals. Using this, patients can connect with doctors and physicians remotely and seek 24/7 support related to their diagnosis, diet schedules, appointment scheduling and more. It can also minimize operational expenses and offer affordable and accessible services to patients.
2. Brings out insights from medical datasets in near real-time
The healthcare industry generates unstructured data from disparate sources like patient records, billings, scheduling, pharmaceutical companies, government regulations, and others. Getting actionable insights manually from these in near real-time is challenging.
By providing easy access to previous records and predictive analytics, AI can speed up the process of diagnosis and inspire timely treatment. A few years back, AI interpreted medical images from EHRs to provide detection of cancerous cells. Since then, it has made galactic leaps in diagnosis. AI chatbots like LungDiag are showing promising signs of diagnostic abilities.
Manual scheduling processes are often time-consuming and prone to errors. But virtual assistants can help people schedule their appointments based on the need and availability of physicians. With these, healthcare providers can keep patients engaged, reduce no-shows, and optimize schedules to increase productivity and revenue.
There’s also another benefit. Healthcare providers can spare more time to patient care than in administrative tasks by automating the scheduling process. It can further improve a patient’s experience by removing the need to visit healthcare facilities all the time.
AI’s ability to read datasets and analyze to support prior authorization (PA) can also improve patient treatment and experience. It can ensure that patients receive the appropriate care for their needs in sync with the latest medical evidence and guidelines. Healthcare providers can get preapproval from patients to administer a service or a medication. This process can prevent inappropriate service utilization and ensure patients get the first-line treatments before receiving more invasive or risky therapies.
3. Accelerates pharmaceutical development
Before the COVID-19 vaccine, the fastest vaccine discovered was for Mumps in the 1960s. That discovery took four years but the groundwork was already done during World War 2. With AI and ML technology, researchers launched the first Covid-19 vaccine in less than a year.
Drug discovery is an expensive and competitive affair, and the market is huge. With AI in it, this market can now become even bigger. Pharmaceutical executives in the US healthcare system have realized that AI for medicine can generate nearly $100B annually. This is one of the reasons why top pharmaceutical companies are implementing AI in the manufacturing process. They are further leveraging its ability to reduce research and development costs.
Besides, AI can perform quality checks, minimize material waste, enhance production reuse and ensure better predictive maintenance. In the supply-chain side of the sector, ML models can prevent situations of over-demand and under-demand, along with managing supply-chain problems and failures in the production line.
4. Identifies dosage errors and prevents fraud
People often forget to take medicines or they take it more than needed. For instance, following the exact process of taking insulins. A lot of diabetic patients forget to take them. This is a concern, especially for geriatric populations who tend to forget more, as a slight error in medicine intake can be fatal. But AI-enabled wireless sensing devices can share immediate alerts when the patient administers insulin or inhaler inappropriately.
Among various benefits of AI in healthcare, its ability to detect fraud can be a game-changer. Each year, fraudulent activities, including wastage of resources, false claims, bribes, and risking patients’ lives by providing unrequired care, cause losses of billions of US dollars.
Consumers’ medical insurance is also vulnerable to data breaches and unlawful practices. It makes identifying claims before reimbursement crucial. But healthcare records are difficult to cross-check and investigators can’t monitor transactions manually in real-time. AI can help by identifying unusual patterns of insurance claims, such as billing for unperformed costly procedures and undergoing unnecessary tests to claim for insurance payments.
5. Increases precision of surgeries with robotics
In 2017, the Maastricht University Medical Centre in the Netherlands used AI robots to join small blood vessels, not more than .03 millimeters. A surgeon controlled the robot whose hand movements were converted into more precise activities.
Robotic surgeries can transform the way surgeons function. One, it can kill the distance- with a better network, doctors can control robotic arms to perform serious surgeries with more precision, that too, from a remote location. It will help the medical industry reach out to people staying in distant locations. Two, it can increase precision and assist surgeons in surgeries requiring strength, like in the orthopedic department.
Robots can operate in tiny spaces. They can reduce the need for open surgery. They can be more accurate around sensitive tissues and organs, reduce the risk of blood loss and infection, and post-surgery complications. Patients have also reported less scarring and faster recovery time compared to traditional surgeries.
6. Improves patient prioritization and triage
Assortment of patients and their triage is a tedious process. Medical emergencies often experience long waiting times and managing paperwork during emergencies can be stressful. In the US, patients often get a waiting period of months before they can visit the emergency. One of the major reasons
for such a long waiting period is the patient’s inability to understand when they should visit the emergency.
Doctors and nurses often struggle with prioritizing cases and managing patients. In such scenarios, AI can help with patient intake and triage using voice assistants and chatbots. AI apps can help patients with a basic diagnosis and inform the healthcare providers for better prioritization of cases. Predictive analytics can also boost the process and reduce the waiting period in emergency.
7. Creates collaboration opportunities
AI creates scopes for collaboration among medical professionals, patients and researchers. It is doable with AI-driven platforms that collect and analyze accurate health data from authentic sources and provide insights that can encourage medical advancements.
These collaborative platforms allow medical professionals to share knowledge, exchange best practices and learn from their experiences. On top of that, patients can submit their health data to the research studies, allowing the researchers to test hypotheses and design clinical trials for developing new treatments and therapies.
Just like there is an idea of Yin and Yang in everything, AI also comes with its own challenges. To maximize the benefits of AI in healthcare, you need to learn about its limitations and make strategic implementation.
You May Interested In: Top 10 industries with practical AI use cases
Key challenges of AI in healthcare
Here are the top cons of AI in healthcare:
1. Lack of accurate medical data
Clinicians need detailed datasets for the technical and clinical validation of AI models. However, due to disintegrated medical data across software platforms, gathering authentic patient information and testing AI algorithms can be difficult.
Consolidating these data in countries where they follow siloed data systems can be more challenging. Healthcare organizations must update and maintain digital records in time to avoid these issues and be more efficient and accurate.
Then there are problems related to labeling of data and its transparency. This is affecting the performance of electronic health records or EHRs. The data these systems are getting from diverse sources are often not labeled properly.
2. Issues in privacy and data bias
Privacy is a serious matter when it comes to patient data collection. With hackers trying to access patients’ confidential data, this has become a burning issue for many organizations. Then there are
other types of attacks as well involving data input poisoning and model extraction. The former involves inserting bad data into a training set, impacting model’s output and the latter extracts information about the AI algorithms to develop a substitute model.
To mitigate these threats, healthcare providers should conduct risk analyses and implement security measures such as multi-factor authentication and encryption.
There is data bias as well. For instance, while incorporating data from academic medical centers into the system, the process may not give enough importance to populations from other areas except academic medical centers. To avoid sampling bias and unequal representation of groups in the training data, AI experts need to identify the source and characteristics of the dataset. Even minor variations in the training data or in AI model configuration can lead to severe outcomes.
In a recent event, STAT News investigation has accused EPIC, an EHR vendor of financially incentivizing hospitals and health systems. This is concerning as false predictions can further create problems for AI’s credibility.
3. Flaws in methodological research
There are few established methodologies, prospective research and reviewed studies of AI in healthcare. Most of the studies are based on retrospective analysis and historical patient medical data. However, to understand the potential of AI diagnosis in real-world settings, medical professionals must assess current patients all the time. For reliable prospective research, doctors should observe their patients’ health with physical tests, remote monitoring and telehealth visits.
4. Lack of AI expertise
Since Covid-19, there’s been a huge surge in AI projects across sectors. This has generated a need for a good number of AI experts. But finding these experts has sprung up as a Herculean challenge for businesses. It is even worse for companies that are looking for mavericks with niche skillsets.
The healthcare sector is no different. Hospitals, pharmaceutical companies, and software industries that are building CRMs for these organizations are all facing the heat. In addition, there are limited number of experts who understand both healthcare and AI. To address the shortage, healthcare organizations need to invest in training and education programs that will allow their employees to acquire essential skills.
Read also: All you need to know about the Implementation of AI
AI’s success in the healthcare industry depends a lot on a quick early assessment of the impact areas and experts with knowledge of the domain. Product development teams with the right blend of AI experts, data scientists, developers, and UX designers can simplify the process.
We, at Talentica Software, can help you develop AI-powered products. Our experts have developed more than 30 AI/ML products from diverse sectors and helped businesses solve unique problems.
References:
[1] How Artificial Intelligence is Accelerating Innovation in Healthcare (goldmansachs.com)
[2] AI in healthcare market size worldwide 2030 | Statista